Cutting stainless steel sheet requires specific techniques and tools due to its hardness and durability. This guide covers various methods, from simple hand tools to advanced industrial processes, ensuring precise and safe cutting operations.


Common Cutting Methods:
- Power Shears
Advantages:

- Clean, straight cuts
- Minimal material waste
- No heat affected zone
- Fast operation
- Portable options available
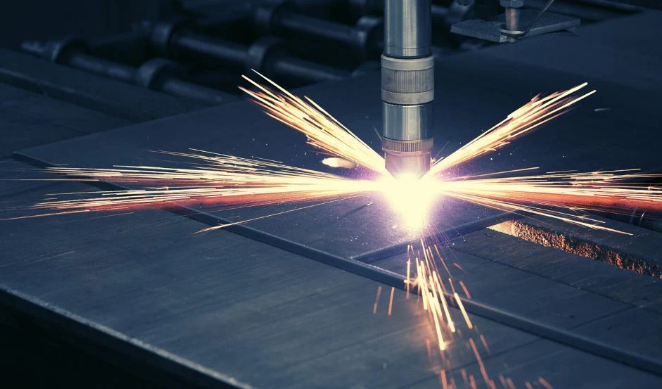
- Plasma Cutting
Benefits
- High cutting speed
- Suitable for thick sheets
- Complex shape capability
- Automated options
- Cost-effective for large projects
- Laser Cutting
Features:
- Highest precision
- Clean edges
- Complex designs possible
- Minimal material waste
- Consistent results
- Water Jet Cutting
Advantages:
- No heat affected zone
- Clean cuts
- Environmental friendly
- Multiple sheet cutting
- Various thickness capability
Hand Tool Methods:
- Aviation Snips
Best for:
- Thin sheets
- Curved cuts
- Small projects
- DIY work
- Detail work
- Circular Saw
Applications:
- Straight cuts
- Medium thickness
- On-site cutting
- Construction work
- Maintenance tasks
Safety Considerations:
- Personal Protection
- Safety glasses
- Cut-resistant gloves
- Steel-toed boots
- Face shield
- Proper workwear
- Workplace Safety
- Ventilation
- Clean workspace
- Proper lighting
- First aid access
- Fire safety equipment
Preparation Steps:
- Material Assessment
- Measure thickness
- Check material grade
- Mark cutting lines
- Plan cutting sequence
- Secure workspace
- Tool Selection
- Based on thickness
- Project requirements
- Available power
- Budget constraints
- Desired finish
Professional Tips:
- Cutting Techniques
- Use appropriate speed
- Maintain steady pressure
- Follow marked lines
- Cool material as needed
- Support sheet properly
- Quality Control
- Check measurements
- Inspect edge quality
- Monitor tool wear
- Maintain equipment
- Document process
Common Challenges:
- Technical Issues
- Heat buildup
- Edge burring
- Material warping
- Tool wear
- Precision control
- Solutions
- Proper cooling
- Right tool selection
- Correct speed setting
- Regular maintenance
- Operator training
Industrial Applications:
- Manufacturing
- Production lines
- Custom fabrication
- Sheet metal work
- Component parts
- Architectural elements
- Construction
- HVAC systems
- Building facades
- Kitchen equipment
- Industrial equipment
- Structural elements
Cost Considerations:
- Equipment Investment
- Tool costs
- Maintenance expenses
- Operating costs
- Training requirements
- Safety equipment
- Operating Expenses
- Material waste
- Labor costs
- Energy consumption
- Consumable items
- Maintenance supplies
Best Practices:
- Preparation
- Clean material
- Sharp tools
- Proper setup
- Clear workspace
- Safety checks
- Execution
- Steady pace
- Regular checks
- Tool maintenance
- Quality control
- Documentation
Future Trends:
- Technology Advancement
- Automated systems
- AI integration
- Precision improvement
- Energy efficiency
- Smart controls
- Industry Development
- New cutting methods
- Enhanced materials
- Better efficiency
- Reduced waste
- Improved safety
Conclusion:
Successful stainless steel sheet cutting requires:
- Proper tool selection
- Correct technique
- Safety awareness
- Quality control
- Regular maintenance
The choice of cutting method depends on:
- Project requirements
- Material specifications
- Budget constraints
- Quality needs
- Production volume
how to cut stainless steel sheet? — This article provides a practical buyer‑focused overview with specifications, selection tips, and on‑site considerations. Explore related topics: blog.
Key Specifications and Standards
- Standards: ASTM / EN / JIS (e.g., ASTM A240/A36, EN 10088/10025, JIS G4304/G3131).
- Surface options: 2B, BA, No.4, HL, mirror; galvanized (electro / hot‑dip).
- Processing: hot‑rolled, cold‑rolled, annealed & pickled, welded or seamless.
- Typical services: slitting, shearing, cut‑to‑length, drilling, beveling, deburring.
- Documentation: MTC, CO, packing list with net/gross weight and heat numbers.
Typical Applications
Construction, machinery, automotive, energy, enclosures and fencing, food equipment (for stainless), and general fabrication. Match grade and finish to corrosion, strength, and appearance requirements.
Selection Guide
- Use certified material with Mill Test Certificate (MTC).
- Confirm standards (ASTM/EN/JIS) and tolerances per drawing.
- Match surface finish to application (2B/BA/No.4/galvanized).
- Specify dimensions and acceptable deviation upfront.
- Plan packaging and corrosion protection for transit.
Processing, Packaging and Logistics
We adopt edge protection, waterproof wrapping, rust‑inhibiting paper, fumigated pallets, and strapping suitable for sea freight. Loading photos and weight lists are provided for each shipment.
FAQs
Q: What lead time can I expect?
A: Typically 7–15 days ex‑works for standard sizes; custom processing may extend the schedule.
Q: Can you provide cut‑to‑size service?
A: Yes. We slit, shear, cut, drill, bevel and deburr to drawing to reduce waste and speed installation.
Q: How do you ensure quality?
A: Incoming inspection, process control, and final inspection with traceable heat numbers; third‑party inspection is available.
Q: Do you support small trial orders?
A: We support pilot quantities with consolidated shipping to control cost.
All values are typical and for guidance only; confirm with the datasheet and purchase order before production.
Related products: view details.
Related products: view details.


