## The Ubiquitous and Versatile: Standard Sizes of Stainless Steel Rectangular Tubes


Stainless steel rectangular tubes, with their inherent strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, are ubiquitous in countless applications across diverse industries. Understanding the standard sizes available is crucial for engineers, designers, and fabricators alike, ensuring efficient project planning and material selection. This article will delve into the complexities and considerations surrounding standard sizes of stainless steel rectangular tubes.
The term “standard size” itself is somewhat fluid. There isn’t a single, universally agreed-upon standard across all manufacturers and regions. Dimensions are often dictated by the relevant national or international standards organizations like ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), EN (European Norms), or JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards). Furthermore, variations exist based on the tube’s wall thickness, impacting the overall weight and strength. Manufacturers often maintain their own catalogs outlining their available profiles, often with slight deviations from these broader standards.
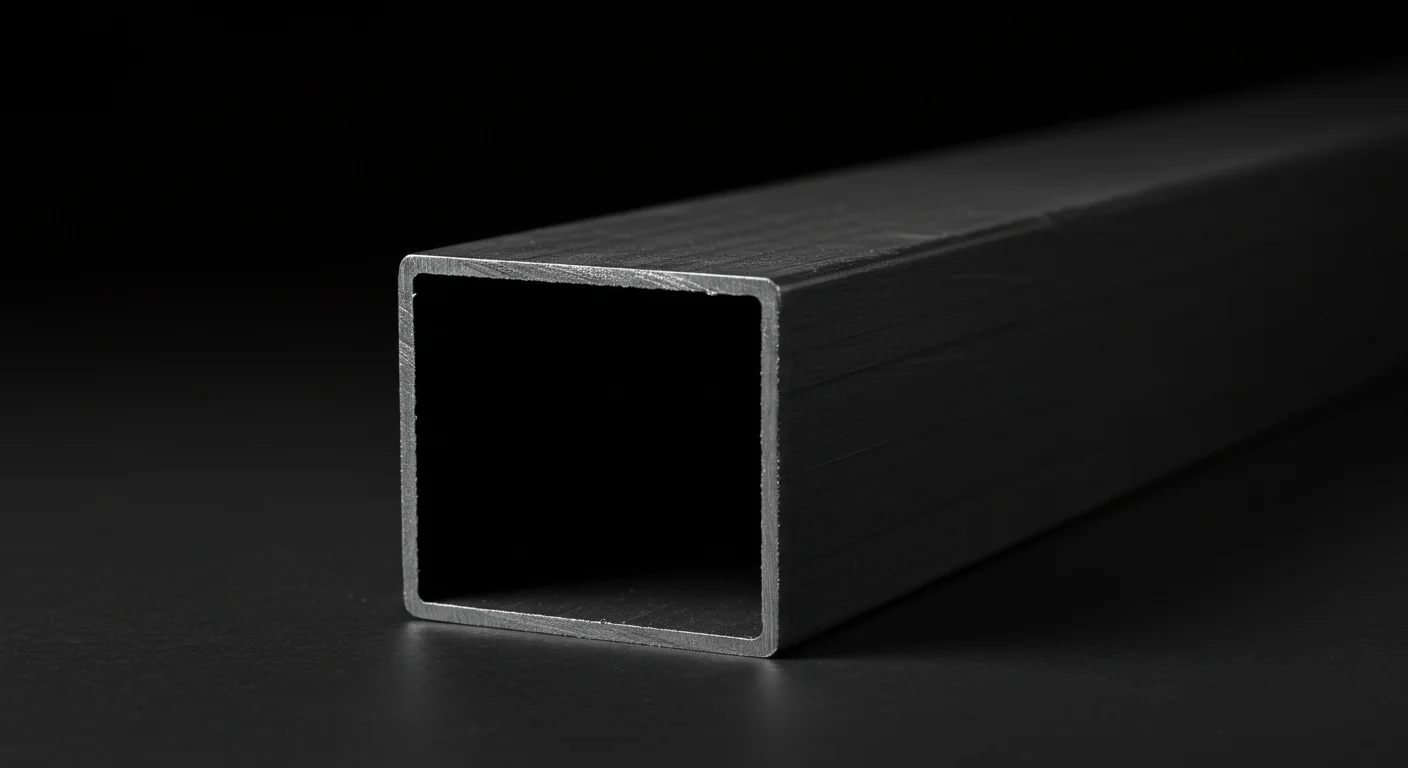
Typically, standard sizes are expressed in terms of the outer dimensions – the length, width, and wall thickness – usually in millimeters or inches. For instance, a common size might be 25x50x2mm, indicating a tube with an outer width of 50mm, an outer height of 25mm, and a wall thickness of 2mm. The length is typically variable and ordered according to project needs, often in multiples of standard lengths, like 6 meters.
The range of available standard sizes is considerable, varying from small profiles used in intricate furniture designs and medical equipment to larger sections employed in structural applications, architectural features, and heavy-duty industrial machinery. Factors influencing the selection of a specific size include:
* **Structural integrity:** The tube’s dimensions and wall thickness directly impact its load-bearing capacity and resistance to bending and torsion.
* **Application requirements:** The size must be suitable for its intended purpose, considering factors like space constraints, weight limitations, and aesthetic considerations.
* **Cost-effectiveness:** Oversizing a tube increases material costs unnecessarily. Choosing the smallest size that meets the structural requirements is crucial for economical design.
* **Availability:** Not all sizes are readily available from every supplier. Selecting a readily available standard size minimizes lead times and procurement difficulties.
Furthermore, the grade of stainless steel also impacts the characteristics of the tube. Common grades like 304 (austenitic) and 316 (austenitic, with increased resistance to chloride corrosion) influence the material’s strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific environments. The choice of grade should always be informed by the application’s demands.
In conclusion, while a definitive list of standard sizes for stainless steel rectangular tubes is unattainable due to the variations across manufacturers and standards, understanding the fundamental principles behind size selection is paramount. Consult manufacturer catalogs and relevant standards to determine the appropriate size for a given project, balancing structural needs, cost, availability, and the specific demands of the intended application. Careful consideration of these factors ensures the successful and efficient utilization of these highly versatile components.
Standard Sizes of Stainless Steel Rectangular Tubes: A Comprehensive Guide — This article provides a practical buyer‑focused overview with specifications, selection tips, and on‑site considerations. Explore related topics: blog.
Key Specifications and Standards
- Standards: ASTM / EN / JIS (e.g., ASTM A240/A36, EN 10088/10025, JIS G4304/G3131).
- Surface options: 2B, BA, No.4, HL, mirror; galvanized (electro / hot‑dip).
- Processing: hot‑rolled, cold‑rolled, annealed & pickled, welded or seamless.
- Typical services: slitting, shearing, cut‑to‑length, drilling, beveling, deburring.
- Documentation: MTC, CO, packing list with net/gross weight and heat numbers.
Typical Applications
Construction, machinery, automotive, energy, enclosures and fencing, food equipment (for stainless), and general fabrication. Match grade and finish to corrosion, strength, and appearance requirements.
Selection Guide
- Use certified material with Mill Test Certificate (MTC).
- Confirm standards (ASTM/EN/JIS) and tolerances per drawing.
- Match surface finish to application (2B/BA/No.4/galvanized).
- Specify dimensions and acceptable deviation upfront.
- Plan packaging and corrosion protection for transit.
Processing, Packaging and Logistics
We adopt edge protection, waterproof wrapping, rust‑inhibiting paper, fumigated pallets, and strapping suitable for sea freight. Loading photos and weight lists are provided for each shipment.
FAQs
Q: What lead time can I expect?
A: Typically 7–15 days ex‑works for standard sizes; custom processing may extend the schedule.
Q: Can you provide cut‑to‑size service?
A: Yes. We slit, shear, cut, drill, bevel and deburr to drawing to reduce waste and speed installation.
Q: How do you ensure quality?
A: Incoming inspection, process control, and final inspection with traceable heat numbers; third‑party inspection is available.
Q: Do you support small trial orders?
A: We support pilot quantities with consolidated shipping to control cost.
All values are typical and for guidance only; confirm with the datasheet and purchase order before production.
Related products: view details.
Related products: view details.








Leave a Reply